Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kasahara, Takamitsu*; Takigami, Machiko*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Prawitwong, P.*; Takigami, Shoji*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 33(4), p.927 - 930, 2008/12
Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) forms a gel when mixed with acid as a result of replacement of sodium in carboxymethyl group with hydrogen; hydrogen bonds are formed among CMC molecules. CMC gel gets new property by mixing with other materials. Konjac mannan (KM) is a water soluble glucomannan with high molar mass and has high viscosity in low concentration aqueous solution. CMC gel is expected to have more elasticity by mixing with KM. Novel CMC-KM mixture gel is made by two processes; (1) mixing CMC with KM solution, (2) immersion of CMC-KM mixture in hydrochloric acid aqueous solution. Interaction of CMC and KM was studied by using KM with different molar mass. Molar mass of KM easily decreases by  -irradiation. The effect of KM molar mass on characteristics of CMC-KM mixture is examined using tensile test fixture.
-irradiation. The effect of KM molar mass on characteristics of CMC-KM mixture is examined using tensile test fixture.
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Abe, Hiroshi; Oshima, Takeshi; Morimoto, Ryo*; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Mizuki, Junichiro
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 33(4), p.1053 - 1056, 2008/12
The effect of ion irradiation on palladium (Pd) metal was investigated by hydrogen-absorption measurements, SEM microscopy and synchrotron X-ray diffraction. N irradiation was made with an acceleration energy 350 keV. The initial hydrogen absorption rate of the irradiated Pd was three times larger than that of non-irradiated Pd. The microscopic structure was investigated by using the pair-distribution function (PDF) obtained by X-ray diffraction. Although the average structure of the Pd was f.c.c, the Pd atoms displaced and two occupancy sites are revealed. This site occupancy is closely related with the hydrogen-absorption rate.
irradiation was made with an acceleration energy 350 keV. The initial hydrogen absorption rate of the irradiated Pd was three times larger than that of non-irradiated Pd. The microscopic structure was investigated by using the pair-distribution function (PDF) obtained by X-ray diffraction. Although the average structure of the Pd was f.c.c, the Pd atoms displaced and two occupancy sites are revealed. This site occupancy is closely related with the hydrogen-absorption rate.
Inoue, Aichi; Yamamoto, Shunya; Nagata, Shinji*; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Shikama, Tatsuo*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 33(4), p.1127 - 1130, 2008/12
We investigated effects of catalyst on gasochromic properties in tungsten oxide films. Amorphous WO films coated with Pd and Pt catalysts were prepared on SiO
films coated with Pd and Pt catalysts were prepared on SiO substrates by employing reactive RF magnetron sputtering. The field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM) showed that particles with a dozes nm diameter of Pd and with a few nm of Pt grew on the surface at beginning of deposition. The continuous catalytic layers were observed with increasing the amounts of more than 2 nm for Pd and 0.2 nm for Pt catalysts, respectively. When the continuous layers formed on WO
substrates by employing reactive RF magnetron sputtering. The field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM) showed that particles with a dozes nm diameter of Pd and with a few nm of Pt grew on the surface at beginning of deposition. The continuous catalytic layers were observed with increasing the amounts of more than 2 nm for Pd and 0.2 nm for Pt catalysts, respectively. When the continuous layers formed on WO surface, the excellent gasochromic properties were obtained. The results indicated that Pt catalysts were suitable for high sensitive hydrogen sensors consisting of gasochromic WO
surface, the excellent gasochromic properties were obtained. The results indicated that Pt catalysts were suitable for high sensitive hydrogen sensors consisting of gasochromic WO films.
films.
Sugimoto, Masaki; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Tsukuda, Satoshi*; Seki, Shu*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 33(4), p.1027 - 1030, 2008/12
We have succeeded in synthesizing the silicon carbide (SiC) nano fibers from Si-based polymers using MeV-order heavy-ion beam irradiation technique. Si-based polymers were cross-linked along ion tracks of nano-size in diameter through the whole thickness of the polymer thin film. nano fibers were developed on the surface of the substrate by dissolution and washing away of un-crosslinked polymer by solvent. Subsequent pyrolysis converted polymeric into inorganic SiC nano fibers. The diameter of nano fibers was depended on LET (liner energy transfer), molecular weight and cross-linking efficiency of the precursor polymers.
Takigami, Machiko*; Amada, Haruyo*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Hiroki, Akihiro; Kasai, Noboru; Yoshii, Fumio; Tamada, Masao
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 33(4), p.849 - 852, 2008/12
Shortage of phosphorus becomes a serious problem in the world. The removal of phosphorus in swine urine is a big concern for the environmental conservation. To solve both problems, absorbent to absorb phosphorus in swine urine was developed using carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and Iron. The gel formation proceeded instantaneously when CMC and Iron (III) chloride were mixed, while gel was not formed immediately when Iron (II) chloride was used. Oxidation of Iron (II) to Iron (III) occurs gradually in Iron (II) aqueous solution. However, addition of CMC to the Iron (II) solution promoted the oxidation to form gel. The rate of gel formation could be controlled by addition of acid to CMC-Iron (II) mixture. The resultant gel absorbed phosphorus in swine urine. The absorption was about 97% in swine urine containing 78 mg/L of phosphorus.
Yamazaki, Tatsuya; Asaoka, Hidehito; Takeda, Masayasu; Yamazaki, Dai; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Torikai, Naoya*; Toyoshima, Yasutake*; Shamoto, Shinichi
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 33(3), p.611 - 614, 2008/09
Strontium and SrO are well-known templates on Si for SrTiO , highly-desirable transistor gate material. When stacked on Si, Srlayer becomes amorphous due to its large lattice mismatch of 12%. By introducing a monatomic hydrogen layer on Si, we succeeded in making the Sr (and subsequent SrO) layer(s) grow epitaxially with atomically abrupt interface. However, it is some what mysterious how the monatomic hydrogen layer behaves to manage this large mismatch. In order to identify its behavior, we have employed compound analysis by neutron reflectometer as well as multiple-internal-reflection fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (MIR-FTIR) to investigate the buried heterointerface of Sr grown on Si(111)1
, highly-desirable transistor gate material. When stacked on Si, Srlayer becomes amorphous due to its large lattice mismatch of 12%. By introducing a monatomic hydrogen layer on Si, we succeeded in making the Sr (and subsequent SrO) layer(s) grow epitaxially with atomically abrupt interface. However, it is some what mysterious how the monatomic hydrogen layer behaves to manage this large mismatch. In order to identify its behavior, we have employed compound analysis by neutron reflectometer as well as multiple-internal-reflection fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (MIR-FTIR) to investigate the buried heterointerface of Sr grown on Si(111)1 1: monohydride. We have found difference between the H- and D-terminated substrates in the reflectivity profiles, and changes in Si-H bonding features with the Sr growth (mainly at the initial monolayer stage) in the FTIR spectra. From these, existence of buried H layer at the heterointerfaceis confirmed with its bonding environment.
1: monohydride. We have found difference between the H- and D-terminated substrates in the reflectivity profiles, and changes in Si-H bonding features with the Sr growth (mainly at the initial monolayer stage) in the FTIR spectra. From these, existence of buried H layer at the heterointerfaceis confirmed with its bonding environment.
Makabe, Takeshi*; Prawitwong, P.*; Takahashi, Ryo*; Takigami, Machiko*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Takigami, Shoji*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 33(2), p.471 - 474, 2008/06
Konjac mannan (KM) is a water soluble glucomannan with high molar mass. KM aqueous solution shows extremely high viscosity. The effects of  -rays irradiation and acid hydrolysis on molar mass were studied. The hydrolysis was carried out using citric acid. Characteristics of the irradiated and hydrolyzed KM were investigated using GPC-MALLS and a viscometer. The chemical structure of KM scarcely changed by both treatments. Molar mass of the irradiated KM decreased gradually with increasing dose. Molar mass of the hydrolyzed KM also decreased gradually with acid concentration. The viscosity of both treated KM aqueous solutions decreased with decreasing molar mass. High molar mass KM solution showed pseudo-plastic fluids behavior of the non-Newtonian fluid at dilute region and changed to Newtonian fluid with decrease of molar mass. Low molar mass KM solution showed behavior of Newtonian fluid at semi-dilute region. The critical concentration at the overlap limit of KM solution increased with decreasing of molar mass.
-rays irradiation and acid hydrolysis on molar mass were studied. The hydrolysis was carried out using citric acid. Characteristics of the irradiated and hydrolyzed KM were investigated using GPC-MALLS and a viscometer. The chemical structure of KM scarcely changed by both treatments. Molar mass of the irradiated KM decreased gradually with increasing dose. Molar mass of the hydrolyzed KM also decreased gradually with acid concentration. The viscosity of both treated KM aqueous solutions decreased with decreasing molar mass. High molar mass KM solution showed pseudo-plastic fluids behavior of the non-Newtonian fluid at dilute region and changed to Newtonian fluid with decrease of molar mass. Low molar mass KM solution showed behavior of Newtonian fluid at semi-dilute region. The critical concentration at the overlap limit of KM solution increased with decreasing of molar mass.
 Nb
Nb )O
)O
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Yasuda, Naohiko*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 33(1), p.15 - 18, 2008/03
Pb 
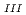 -edge absorption spectra of ordered and disordered Pb(In
-edge absorption spectra of ordered and disordered Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O (PIN) were analyzed. The absorption edges of both the ordered and disordered PIN were shifted depending on the thermal condition of post-annealing. A clear edge shift was observed between the ordered and disordered PIN crystals. The local environments of the Pb atoms were different in these PIN crystals. This edge shift can be interpreted by introducing disarrangement of B-site atoms. Disordering of B-site atoms has not only an effect on the local bond distribution but also an effect on the long-range order crystal structure.
(PIN) were analyzed. The absorption edges of both the ordered and disordered PIN were shifted depending on the thermal condition of post-annealing. A clear edge shift was observed between the ordered and disordered PIN crystals. The local environments of the Pb atoms were different in these PIN crystals. This edge shift can be interpreted by introducing disarrangement of B-site atoms. Disordering of B-site atoms has not only an effect on the local bond distribution but also an effect on the long-range order crystal structure.
 films
filmsYamamoto, Shunya; Inoue, Aichi; Sugimoto, Masaki; Takano, Katsuyoshi; Nagata, Shinji*; Yoshikawa, Masahito
no journal, ,
We investigated the effects of ion irradiation on the crystalline structure and the gasochromism of tungsten oxide (WO ) films. Stoichiometric WO
) films. Stoichiometric WO films (thickness: 300 nm) were prepared by reactive rf magnetron sputtering and subsequent annealing at a temperature of 400
films (thickness: 300 nm) were prepared by reactive rf magnetron sputtering and subsequent annealing at a temperature of 400  C in air. Ion irradiations with 350 keV helium and oxygen were performed in a fluence up to 1
C in air. Ion irradiations with 350 keV helium and oxygen were performed in a fluence up to 1 10
10 cm
cm . The films are characterized by X-ray diffraction and Raman scattering spectroscopy. After the ion irradiations, the gasochromic coloration of WO
. The films are characterized by X-ray diffraction and Raman scattering spectroscopy. After the ion irradiations, the gasochromic coloration of WO films coated with a Pd-catalyst was examined by optical transmission exposure to 1% hydrogen in argon gas. WO
films coated with a Pd-catalyst was examined by optical transmission exposure to 1% hydrogen in argon gas. WO films irradiated with 350 keV
films irradiated with 350 keV  O
O ions (fluence: 5
ions (fluence: 5 10
10
 5
5  10
10 cm
cm  ) exhibit good gasochromic coloration. The results suggest that improvement of gasochromic coloration is related to the amorphization with introducing appropriate amount of defects such as oxygen vacancies.
) exhibit good gasochromic coloration. The results suggest that improvement of gasochromic coloration is related to the amorphization with introducing appropriate amount of defects such as oxygen vacancies.
Miura, Kenta*; Tanemura, Tsuyoshi*; Hommi, Masashi*; Hanaizumi, Osamu*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Takano, Katsuyoshi; Sugimoto, Masaki; Yoshikawa, Masahito
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takeda, Masayasu; Yamazaki, Dai; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Hirano, Tatsumi*
no journal, ,
The X-ray and neutron reflectometries have now widely used for the study of buried interfaces in thin films and multilayers. Neutron is an ideal probe for the reflectometry because of its transparency for the most of materials, and its sensitivity of light elements and magnetic moments in the materials. An intense pulsed neutron source (JSNS) is now under construction at Materials and Life Science Facility (MLF) as a part of J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex) in Tokai-mura, Ibaraki prefecture, Japan. JSNS will provide the world highest intensity pulsed neutron for promoting materials science and life science in the beginning of the next spring. We have sent a letter of intent which proposed to construct a polarized neutron reflectometer at MLF to the director of J-PARC, and a preliminary examination has been passed. The outline design specification of this new polarized neutron reflectometer will be presented.
 -irradiation on mixtures of DNA and bovine serum albumin
-irradiation on mixtures of DNA and bovine serum albuminSaito, Hiroyuki*; Furusawa, Kazuya*; Dobashi, Toshiaki*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu
no journal, ,
Halogenated aromatic compounds, such as dioxin and polychlorinated biphenyl, result in cancer and reproductive anomaly through intercalation into the major grooves and interstices between base pairs of double helical DNA. Water-insoluble DNA-based materials can be utilized as the most efficient adsorbents of such toxic agents. In this study, we have successfully prepared DNA-bovine serum albumin (BSA) hybrid gels from aqueous mixtures of DNA with BSA by  -ray irradiation. We have characterized the gel property and adsorption property of DNA-BSA hybrid gels. The interesting result that mixing
-ray irradiation. We have characterized the gel property and adsorption property of DNA-BSA hybrid gels. The interesting result that mixing  -ray-scission polymers of DNA and BSA changes them to be
-ray-scission polymers of DNA and BSA changes them to be  -ray-crosslinking materials is discussed.
-ray-crosslinking materials is discussed.
 -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationFurusawa, Kazuya*; Kita, Erika*; Saheki, Toshihiko*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Nishi, Norio*; Dobashi, Toshiaki*
no journal, ,
To insolubilize DNA for preparing a novel carcinogen adsorbent, effects of  -ray irradiation on aqueous solutions of mixtures of DNA with radiation-induced crosslinking-type biopolymers (RCBP) such as Type A gelatin, bovine serum albumin (BSA), carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and Catinal (hydroxyethyl-cellulose, O-[2-hydroxy-3- (trimethyl ammonio)-propyl], chloride) have been studied. DNA-RCBP hybrid gels were successfully prepared from aqueous mixtures of DNA with RCBP in a limited range of irradiation dose. Gel fraction (Gf) and swelling ratio (S) of the hybrid gels were measured. The Gf and S of hybrid gels increased and decreased, respectively, with increasing irradiated dose. Adsorption of one of carcinogen, acridine orange, was also examined for the gels. From the experimental results, the optimum condition for preparing insolubilized homogeneous DNA gels was determined.
-ray irradiation on aqueous solutions of mixtures of DNA with radiation-induced crosslinking-type biopolymers (RCBP) such as Type A gelatin, bovine serum albumin (BSA), carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and Catinal (hydroxyethyl-cellulose, O-[2-hydroxy-3- (trimethyl ammonio)-propyl], chloride) have been studied. DNA-RCBP hybrid gels were successfully prepared from aqueous mixtures of DNA with RCBP in a limited range of irradiation dose. Gel fraction (Gf) and swelling ratio (S) of the hybrid gels were measured. The Gf and S of hybrid gels increased and decreased, respectively, with increasing irradiated dose. Adsorption of one of carcinogen, acridine orange, was also examined for the gels. From the experimental results, the optimum condition for preparing insolubilized homogeneous DNA gels was determined.
Takeno, Hiroyuki*; Mochizuki, Tomoyoshi*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu
no journal, ,
We investigated effects of electron beams (EB)-irradiation on miscibility of poly(2-chlorostyrene) and poly(vinyl methyl ether) blends having a lower critical solution temperature type of phase diagram. EB-irradiation in the range of 20 to 50 kGy produced cross-linking with an increase in the molecular weight, while it at a dose of 100 kGy caused both cross-linking and chain scission with a decrease in the molecular weight. However, gel fractions of all the irradiated blends were very low. Cloud points (temperatures) and the Flory-Huggins interaction parameter were obtained for the irradiated blends. The result showed that the miscibility of the blends became slightly worse with increase of the EB-irradiation.
 Nb
Nb )O
)O ; Inelastic X-ray scattering in control of the B-site randomness
; Inelastic X-ray scattering in control of the B-site randomnessOwada, Kenji; Hirota, Kazuma*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Baron, A.*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*
no journal, ,
Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O (PIN) varies among antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) and relaxor states depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. We studied the effects of this randomness on the dynamics of PIN by high resolution inelastic X-ray scattering using ordered PIN (AFE) and disordered PIN (relaxor) single crystals. We have found a clear softening of a transverse optic mode at the
(PIN) varies among antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) and relaxor states depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. We studied the effects of this randomness on the dynamics of PIN by high resolution inelastic X-ray scattering using ordered PIN (AFE) and disordered PIN (relaxor) single crystals. We have found a clear softening of a transverse optic mode at the  point in both the samples, indicating a robust and intrinsic ferroelectric instability regardless of the actual ground state. We interpret that AFE is stabilized only when In and Nb ions are spatially ordered enough to overwhelm the FE instability. As the B-site randomness becomes larger, AFE is suppressed and the FE ground state starts appearing. Ultimately, the randomness competes with the development of FE regions and blocks a long range FE order, which we believe yields polar nanoregions resulting in relaxor behaviors.
point in both the samples, indicating a robust and intrinsic ferroelectric instability regardless of the actual ground state. We interpret that AFE is stabilized only when In and Nb ions are spatially ordered enough to overwhelm the FE instability. As the B-site randomness becomes larger, AFE is suppressed and the FE ground state starts appearing. Ultimately, the randomness competes with the development of FE regions and blocks a long range FE order, which we believe yields polar nanoregions resulting in relaxor behaviors.